Snow Drift On Gable Roofs

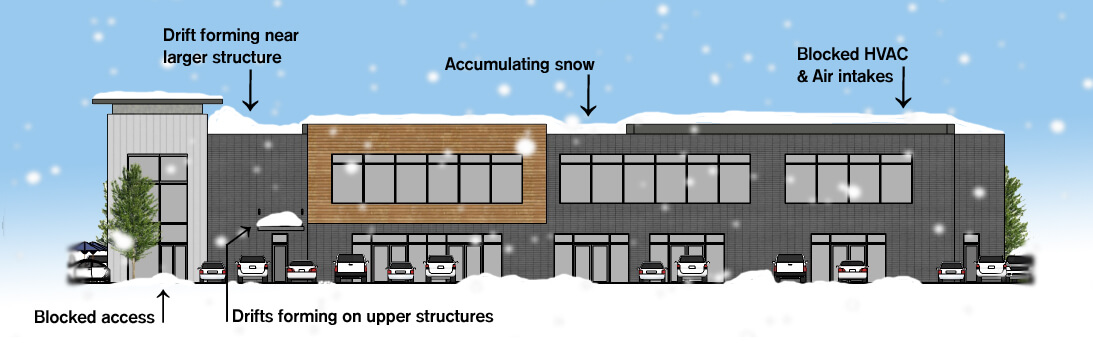
The amount of additional snow load or surcharge depends on the difference in height of the two adjacent roofs and the lengths of roof perpendicular to the drop in height.
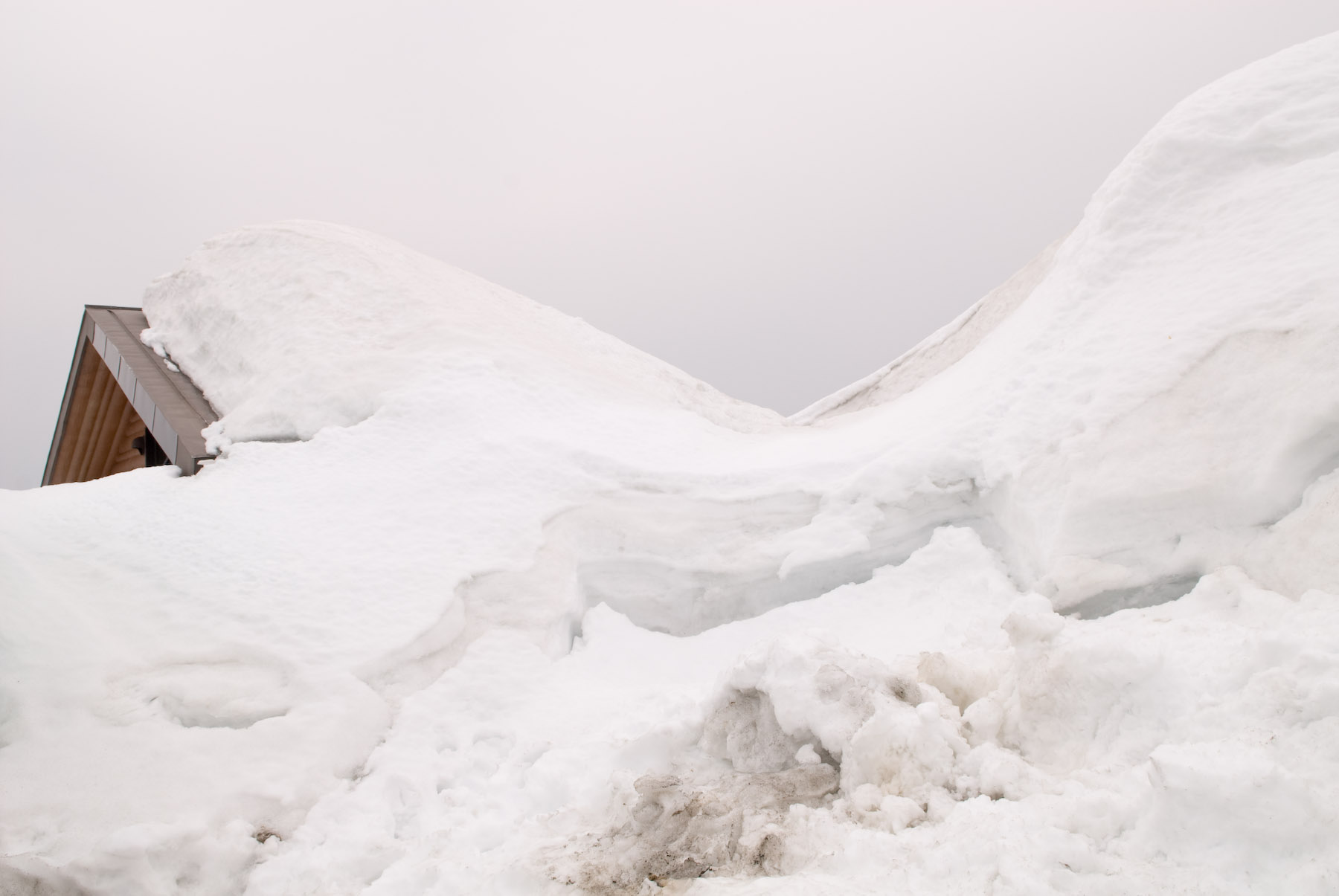
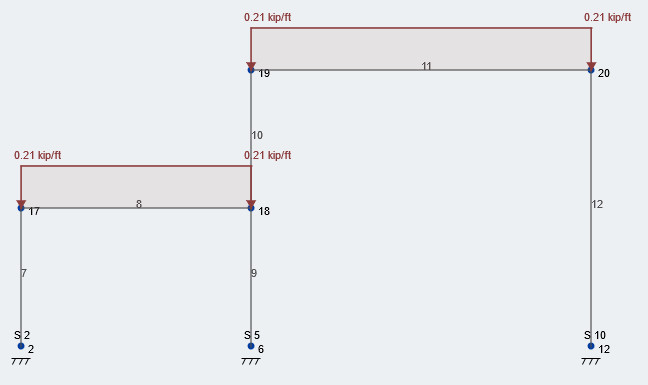
Snow drift on gable roofs. For gable roofs a rectangular drift surcharge was prescribed and the rectangular shape remained unchanged everywhere along the ridge line. The wind causing snow transport and. The gable roof exhibited a slightly higher accumulation coefficient than the flat roof. Gable roof drifts slope limits there is a range of roof slopes which require gable drifts lower limit is on 12 upper limit is 7 on 12 39 gable drifts upper limit observations by ttea unbalance for 6 on 12 less consistent with max slope of roof step drifts 1v 2h angle of repose of drifted snow 30 40.
Resulting drift formation was envisioned as perpendicular to the roof step para pet wall or ridgeline. Gable roof is a typical roof style which is commonly used in many countries. Ground snow drift is a 2 hfor more complex geometries a reasonable approach is to match the cross sectional area of the odd shaped drift to that for a roof step with the same fetch and ground load 50 faq 4 odd drift geometries approach used for gable roof drifts in 7 05 area for roof step d for a triangular gable drift with a. For the case of a roof step where leeward and windward.
In snowy regions an accurate prediction of drifting snow loads on gable roofs is essential for structural designs. An analysis of snowdrift patterns and accumulation coefficients which are representative of the depth of snow cover for flat and gable roofs showed that accumulation coefficient decreases in accordance with increases in wind speed. Windward snow drifts occur when wind blows snow from a lower elevation roof towards the wall of an adjacent higher roof.